In the world of dental laboratories, precision and efficiency are paramount in creating high-quality dental restorations. Among the many tools and materials utilized, diamond discs, stainless steel discs, and stone discs hold significant importance in shaping, finishing, and polishing dental restorations. This article aims to provide valuable insights into the key differences between these disc types, offering guidance for dental professionals and technicians.
Diamond Discs, Stainless Steel Discs and Stone Discs Serve Distinct Purposes in Dental Lab Work

Diamond discs are renowned for their exceptional cutting abilities and are primarily used for fast and precise material removal during shaping and contouring procedures. Their composition includes diamond particles embedded in a metal matrix, making them highly durable and abrasion-resistant.

Stainless steel discs, on the other hand, are versatile tools that find applications in various stages of dental restoration processes. They are known for their cutting efficiency and are commonly used for preliminary contouring and finishing procedures. Stainless steel discs offer durability and are compatible with a wide range of dental materials.

Stone discs, also known as porcelain polishing discs, are specifically designed for the final polishing of dental restorations. Made from a composite material, they provide a gentle yet effective polishing action, resulting in a smooth and lustrous surface. Stone discs are essential in achieving the desired aesthetic appeal and patient satisfaction.
Cutting Efficiency
When comparing cutting efficiency, diamond discs reign supreme. With their high concentration of diamond particles, they offer exceptional material removal rates, precision, and the ability to create smooth surfaces. Stainless steel discs follow closely, delivering efficient cutting performance. Stone discs, while not as aggressive in cutting, excel in providing a superior final polish.
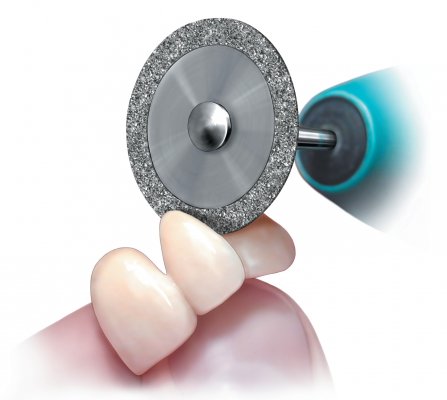

Versatility and Applications
The versatility and applications of these disc types vary significantly. Diamond discs are ideal for shaping and contouring restorative materials such as zirconia, metal alloys, and composite resins. Stainless steel discs find their application in a wide range of procedures, including trimming, reducing excess material, and adjusting metal frameworks. Stone discs, as mentioned earlier, are specifically designed for the final polishing of porcelain restorations, including crowns, veneers, and bridges.
Heat Generation and Cooling
Heat generation during disc usage is a crucial consideration. Diamond discs generate more heat compared to stainless steel and stone discs due to their aggressive cutting action. Proper cooling techniques, such as using water or a coolant spray, are essential to prevent overheating and potential damage to the restoration or the disc itself.
Longevity and Maintenance
In terms of longevity and maintenance, diamond discs tend to have a longer lifespan due to their durable diamond-infused composition. However, their longevity also depends on factors such as disc thickness, quality, and regular cleaning. Stainless steel discs offer good durability and can be easily cleaned and sterilized for reuse. Stone discs, while effective in polishing, may wear out more quickly and require more frequent replacement.
Safety Considerations
Safety considerations should always be a top priority. When using any type of disc, dental professionals should follow proper handling techniques and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) to safeguard against potential hazards. This includes protective eyewear, masks, and gloves.

Cost Analysis
Cost analysis is another crucial aspect to consider. Diamond discs generally require a higher initial investment compared to stainless steel and stone discs. However, their longevity and cutting efficiency may offset the higher upfront cost in the long run. Stainless steel discs are relatively cost-effective and can be reused, while stone discs may require more frequent replacement, adding to the overall expenses.
In conclusion, understanding the differences between diamond discs, stainless steel discs, and stone discs is essential for dental professionals and technicians in achieving optimal results in dental restorations. By considering the purpose, material composition, cutting efficiency, versatility, safety, cost, and maintenance aspects, dental laboratories can make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable disc type for their specific.