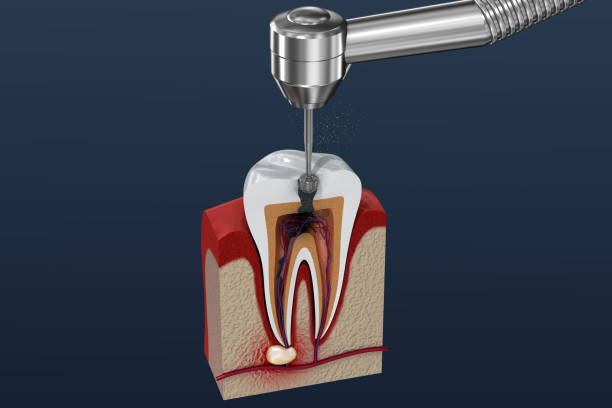
The bur is a consumable tool used by stomologists. It is a very small steel needle. This bur consists of a bur head and a shank. If the dentist's handpiece is likened to a hand-held drill, the bur head is equivalent to the drill bit on the drill. Burs are divided into tungsten carbide burs and diamond burs. Among them, tungsten carbide burs are more commonly used abroad than in China, where emery burs are mainly used by dentists.

Diamond Bur
The diamond bur head has fine diamond particles attached to the periphery of the drill bit. These diamond particles have been processed by decontamination, demagnetization, spheronization, and purification, and have excellent sharpness and wear resistance. During the use of the emery bur, the emery will gradually fall off. Usually, the service life of the diamond bur will end when the emery has fallen halfway.
Tungster carbide
The tungsten carbide bur is formed by welding tungsten carbide powder and cobalt powder by vacuum high temperature sintering or high pressure molding on a steel rod, and is processed and dressed by a large diamond grinding wheel. When the tooth is prepared in this way, the smooth surface makes it easier to get an accurate impression, which leads to a more accurate and close-edged all-ceramic restoration. Tungsten carbide burs meet the requirements for minimally invasive preparation of teeth. Tungsten carbide burs are good at leveling and are great for making fine adjustments to teeth, like making in-place grooves, barrel holes, dove tails, and so on. There are also many choices for the head shape of the diamond bur, such as TF (flat cone), SR (round cylinder), etc.
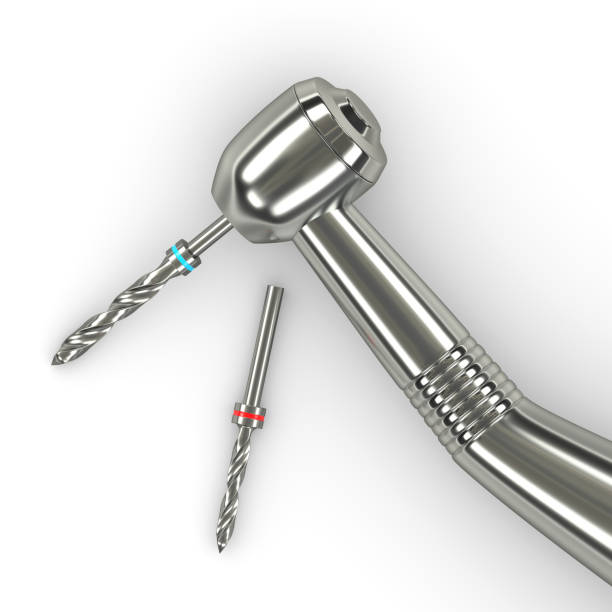
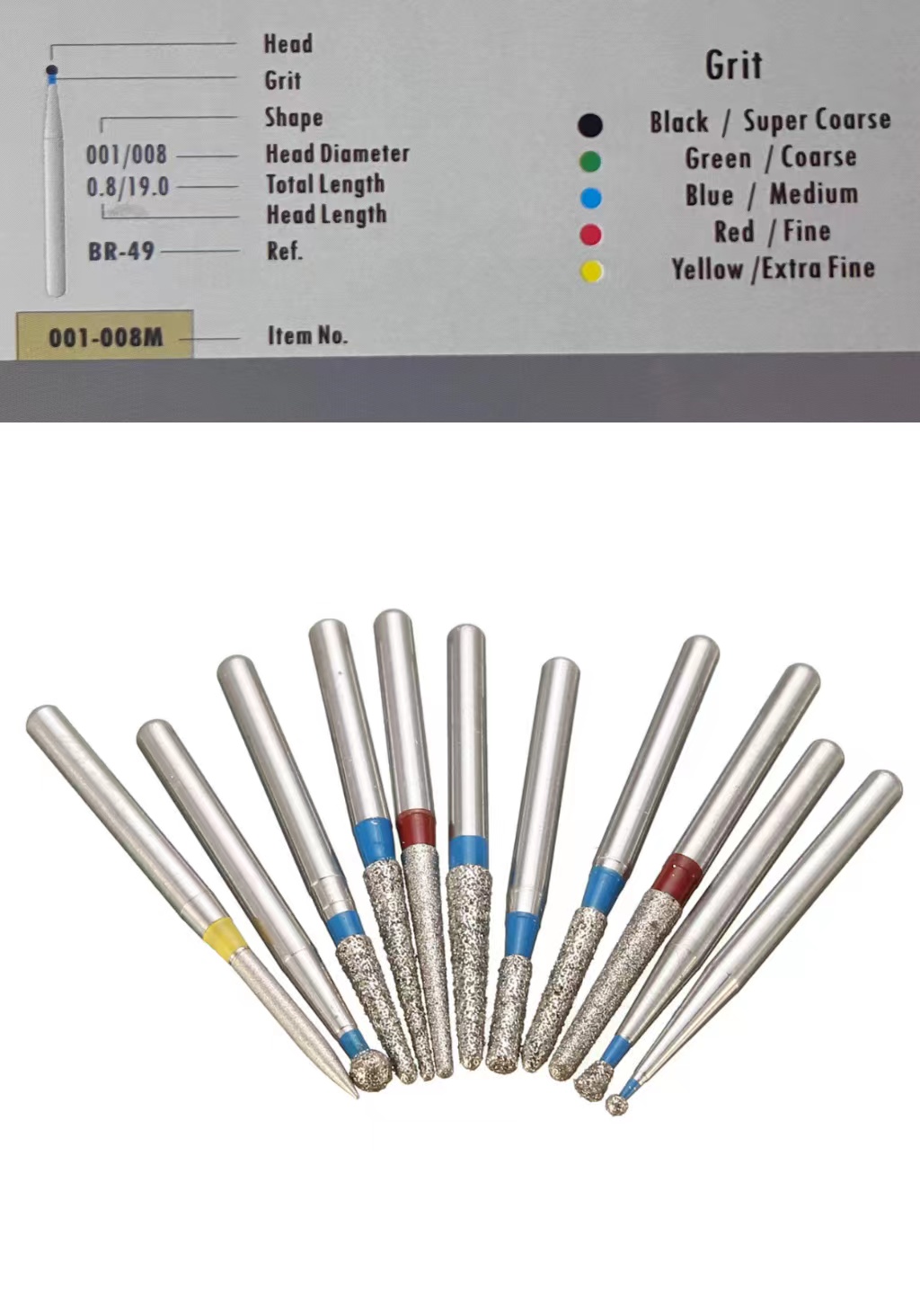
Diamond Bur’s Grit Thickness
At the same time, the grit thickness of the bur grinding head is also very important. From thick to thin, they are: black, green, blue, red, and yellow.
Black: Extra-coarse grinding needle, the particle size is about 150 microns / the number of blades does not exceed 8, and the extra-coarse is expressed in SC.
Green: Roughly polished bur, the particle size is about 125 microns / the number of blades does not exceed 8, with C for coarse.
Blue: Standard grinding needle, the particle size is about 105 microns / the number of blades does not exceed 8. No letter/M means standard.
Red: Fine grinding needle, the particle size is about 45 microns / the number of blades is 10–14, with F for fine.
Yellow: ultra-fine bur, particle size is about 25 microns / number of blades is 16-20. Express ultra-fine by EF or XF.

Because each patient is different and has a different tooth position and proposed restoration method, doctors should be able to choose the right dental preparation tools.
Also, when preparing a tooth well, as few tools and burs as possible should be used. This can cut down on the time it takes and make the patient feel more comfortable.